Using Biosensors for Biomarker Identification and Validation in Lung Cancer

The development of biosensors for the identification and validation of cancer biomarkers has huge potential for accelerating treatment approaches in patients.
This growth comes from advancements in the genomic field, which have facilitated the identification of specific biomarkers previously difficult to detect.
Increasingly, biosensors – analytical devices which convert a biological response into an electrical signal – are demonstrating their value in assisting in biomarker identification, with applications both in health management and treatment.
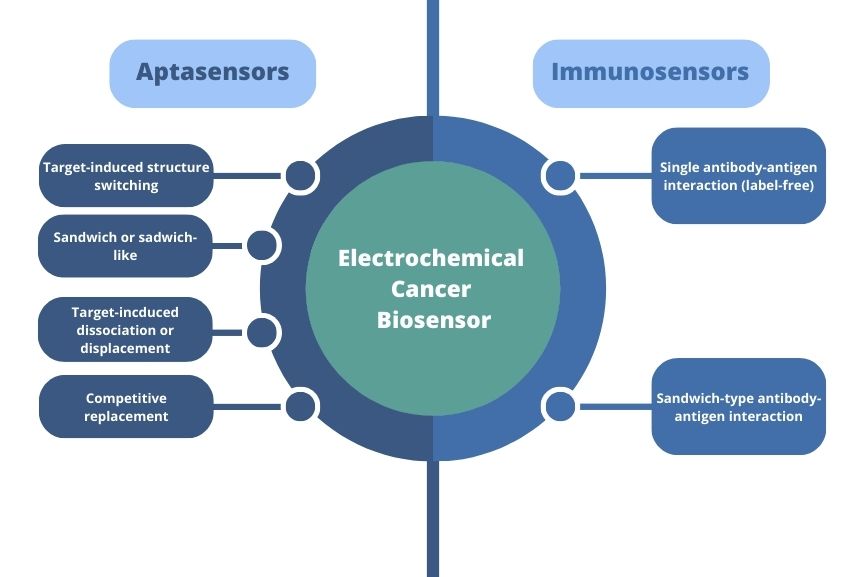
Figure 1. The division between different types of biosensors and their applications.
These can be used to identify cancer biomarkers, which are typically protein biomarkers: by measuring the amount of a biomarker present in a sample through the binding of a labelled antigen, biosensors can detect patient health indicators.
The main appeal of biosensors lies in their ability to provide a fast, cost-effective, reliable, highly-sensitive and easy way to obtain an earlier clinical diagnosis.
Various types of biosensors in use in the medical sphere at present include enzyme-based and tissue-based biosensors.
One major application of biosensors is in the detection of lung cancer biomarkers.
Biosensors in the Identification of Lung Cancer Biomarkers
At present, lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related death.
Part of the reason for this lies in difficulties in detection and diagnosis – chest X-rays display reduced sensitivity in detecting small-sized tumours, which can result in missed diagnoses and delay early detection.
Biosensors utilising transduction techniques may offer a promising solution for the detection of lung cancer biomarkers.
Some key transducing techniques include optical techniques, electrochemical techniques and mass-based techniques for detecting biomarkers and cancer-related volatile organic compounds.
- A Wearable Ultrasound Patch for the Home Detection of Breast Cancer
- Plasma Biomarkers Show Promise in CNS Trials for Alzheimer’s Disease
- Biomarker Strategies for Monitoring the Tumour Microenvironment
Graphene has outstanding properties in its charge transfer, surface area, thermal conductivity, and optical characteristics.
As such, there has been a growing body of research exploring the applications of graphene-based biosensors for the detection of lung cancer biomarkers.
Lung cancer detection could be improved through early detection approaches and timely treatment through the innovation of sensing technologies – particularly biosensors that could provide rapid detection of lung cancer biomarkers.
Get your regular dose of industry news and announcements here, and keep up to date with the latest ‘Industry Spotlight’ posts.
Visit our Biomarkers Portal to learn more about the latest research into spatial omics and its developments. If you’d like to register your interest for Oxford Global‘s upcoming Biomarkers UK conference, click here to download an agenda or register your interest.