Sony and Astellas Team Up to Create Breakthrough ADC Oncology Platform

Earlier this week, Sony Corporation announced they are undertaking a collaborative research agreement with Japan-based Astellas Pharma. The collaboration aims to discover a novel Antibody-Drug conjugate (ADC) platform in oncology using Sony’s unique "Kiravia Backbone.”
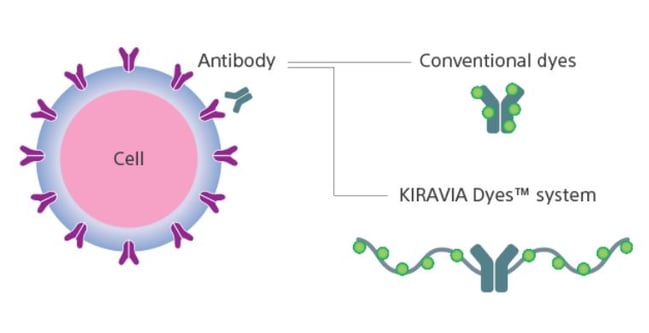
ADCs, a class of therapeutic agents designed to combine the potency of cytotoxic drugs with the specificity of monoclonal antibodies, are a targeted therapy used to treat various diseases and certain cancers. In these structures, the “linker” plays a crucial role, as this serves as the bridge between the monoclonal antibody and the drug. It is designed to be stable in circulation but will undergo specific chemical reactions to release the cytotoxic drug payload once inside the target cell. Effective linkers are crucial to better-performing ADCs.
Sony’s Kiravia backbone, a 3D structure created using an organic polymer technology called Kiravia Dyes, will be the linker for the new ADC platform. The Kiravia backbone is more flexible than other linkers because it is developed using an automatic synthesiser. This results in several beneficial properties, including increased solubility, stability, and capacity than other ADCs, meaning it can carry a significant amount of cytotoxic drug payload.
Sony and Astellas have been in talks regarding platform development since July 2022 and have already completed feasibility studies using human cancer cells. Astellas will now conduct nonclinical trials of development candidates created using Kiravia technology as they begin to build the platform. They hope the platform will lead to the development of anti-cancer drugs with an increased antibody-to-drug ratio with improved stability than currently available ADCs.
In a press release, Katsunori Ogawa, Head of Life Science and Tech Business Unit at Sony Corporation, said that through this collaboration, “Sony is striving to contribute to the medical and drug discovery fields.” He added that they want to provide "further social value by leveraging Sony’s technological capabilities in the development of anti-cancer drugs therapy, which are expected to grow.”
Excitingly, Sony and Astellas do not plan to limit themselves exclusively to the development of ADCs. They have already agreed that they will continue discussions to expand the platform into new areas of cancer drug research. Yoshitsugu Shitaka, CSO at Astellas, has commented that, by continuing to combine Sony’s cutting-edge tech with Astellas’ well-established pharmaceutical capabilities, they hope that the partnership will lead to the “continuous creation of innovative drugs for patients around the world.”
Join Oxford Global’s annual Antibody Engineering 2023: Online event today. This intensive 2-day meeting delves into the latest in antibody engineering and antibody-based therapeutics & a meeting place for experts working within engineering, computational tools and antibody-based therapeutics. Download the agenda to join prominent leaders and scientists as they share new case studies, innovative data, and exciting industry outlooks.







