Cytokines and Immunocytokines in Therapeutic Approaches

Understandings of the design and structure of cytokines have advanced considerably in recent years, improving the veracity of the artificial modulation of cytokine modulation through protein engineering and synthetic immunology.
Cytokines are crucial regulators of the immune system and have pivotal roles in immunity, making them attractive as therapeutics for a variety of immune-related disorders.
Immunocytokines have also received attention in the medical community for their utility in targeted tumoural regulation.
Cytokines typically act via activation of RTK (receptor tyrosine kinase) signalling, whereas immunocytokines target tumour cells through Ab recognition to induce anti-tumour immune responses via cytokine receptor engagement.
However, the widespread use of cytokines in treatment approaches has been limited by their short blood half-lives and severe side-effects caused by low specificity or unfavourable distribution.
If these complications can be overcome, the use of cytokines in immunotherapeutic approaches could broaden the treatment window, particularly for patients with rare diseases that require ‘bespoke’ treatment approaches.
Market Trends in Cytokine Therapeutics
Increases in knowledge associated with cytokine biology converges with new bioengineering approaches to develop engineered cytokine therapeutics, which can be applied to modulate dysregulated immune responses.
Therapeutics arising from the re-engineering of cytokines have been an increasing focus for investment from big-hitting pharmaceutical companies.
Boehringer Ingelheim recently acquired a cytokine therapeutic company to add to their existing portfolio of cancer vaccines, oncolytic viruses, T cell engagers, and other therapeutic modalities.
Trutino Biosciences is a pre-clinical stage biotech company dedicated to the discovery and development of next-gen cytokine therapies.
In parallel, Amunix Pharmaceuticals has been developing T-cell engager and cytokine treatments for solid tumours, which includes the advance of its lead program AMX-818 into the clinic.
Here, the stated goal is to shrink tumours without triggering cytokine release syndrome – an immune overreaction sometimes seen with CAR-T therapies.
Immunocytokines and Therapeutic Applications
Functioning in parallel to cytokine therapies, immunocytokines are antibody-cytokine fusion proteins with the potential to preferentially localise on tumour regions and activate anticancer immunity at the site of disease.
Various tumour targets and antibody formats have been considered for immunocytokine development, including cell membrane antigens, extracellular matrix components, and intact immunoglobulin G (IgG) and antibody fragments.
The first experimental implementations of the immunocytokine concept relied on the use of antibodies in intact IgG formats.
At a later stage, antibody fragments were also considered for product development.
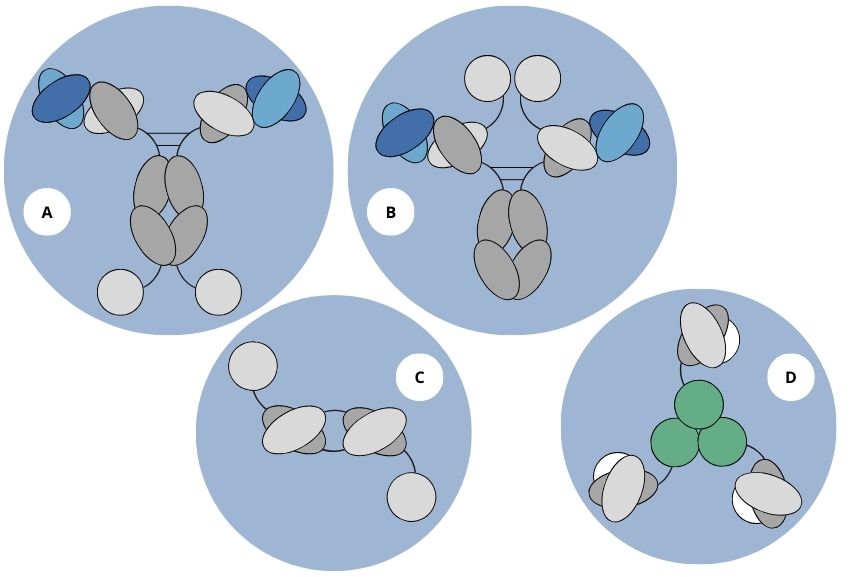
Figure 1. Various antibody formats used for the production of immunocytokines based on IL2, IL12, or TNF (A and B). C represents the diabody-IL2 fusion protein format, while D represents homotrimeric scFv-TNF fusion proteins.
While many cytokine payloads have been considered and tested at the preclinical level, most clinical activities are based on IL2, TNF, and the heterodimeric interleukin-12 (IL12) cytokine.
Both the antibody format and properties of the target antigen can have a profound impact on the performance and mechanism of action of immunocytokine products.
Popular immunocytokine formats entail the genetic fusion of cytokine moieties to various sites on IgG molecules.
Are Health Services Ready?
While immune approaches such as that outlined above are starting to demonstrate promising clinical activity in multiple early phase trials, there are still some hurdles to account for.
As above, these therapies carry the risk of cytokine-mediated on-target/off-tumour adverse events that require highly specialised inpatient facilities.
The field of cancer immunotherapy has grown to encompass new classes of specifically engineered antibodies, which are designed to redirect host immune cells to targeted tumour cells.
- Related: Multispecific Antibody Development: Interview with Yue Liu, President and Founder of Ab Therapeutics
However, CAR-T therapy is and will remain bespoke, with complex and lengthy manufacturing timeframes.
This can be fatally toxic due to issues associated with massive cytokine release and neurotoxicity.
Consequently, the big focus is still on perfecting these immunotherapies without causing severely detrimental harm to the patient.
Get your weekly dose of industry news and announcements here, or head over to our Biologics portal to catch up with the latest advances in targeted therapies. To learn more about our upcoming Biologics UK conference, visit our event website to download an agenda and register your interest.







